Harnessing Nature’s Harmony Exploring Aquaponics Fish Tanks for Sustainable Farming
Table of Contents
Introduction:
In the quest for sustainable and efficient farming practices, aquaponics has emerged as a groundbreaking solution that marries aquaculture and hydroponics to create a harmonious ecosystem. At the heart of this innovative system lies the aquaponics fish tank, a central component that not only provides a habitat for fish but also serves as a catalyst for nutrient-rich water that nourishes plants. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of aquaponics fish tanks, exploring their design, functionality, benefits, and potential applications in sustainable agriculture.
Understanding Aquaponics: A Symbiotic Relationship
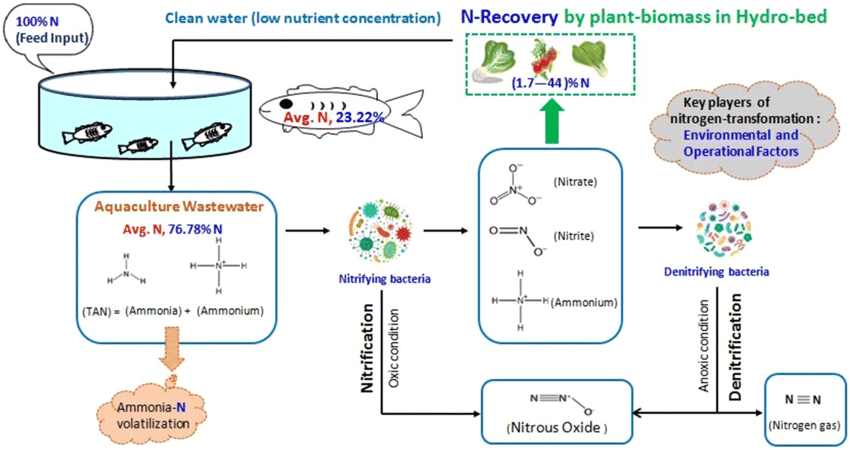
Aquaponics is a closed-loop system that integrates aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics (soil-less plant cultivation) in a symbiotic relationship. In this section, we explore how the aquaponics cycle works, with fish waste serving as a natural fertilizer for plants, and plants acting as natural filters to purify water for fish. We delve into the principles of nutrient cycling, bacteria colonization, and water management that underpin the success of aquaponic systems, highlighting the efficiency and sustainability of this innovative farming method.
The Role of the Aquaponics Fish Tank
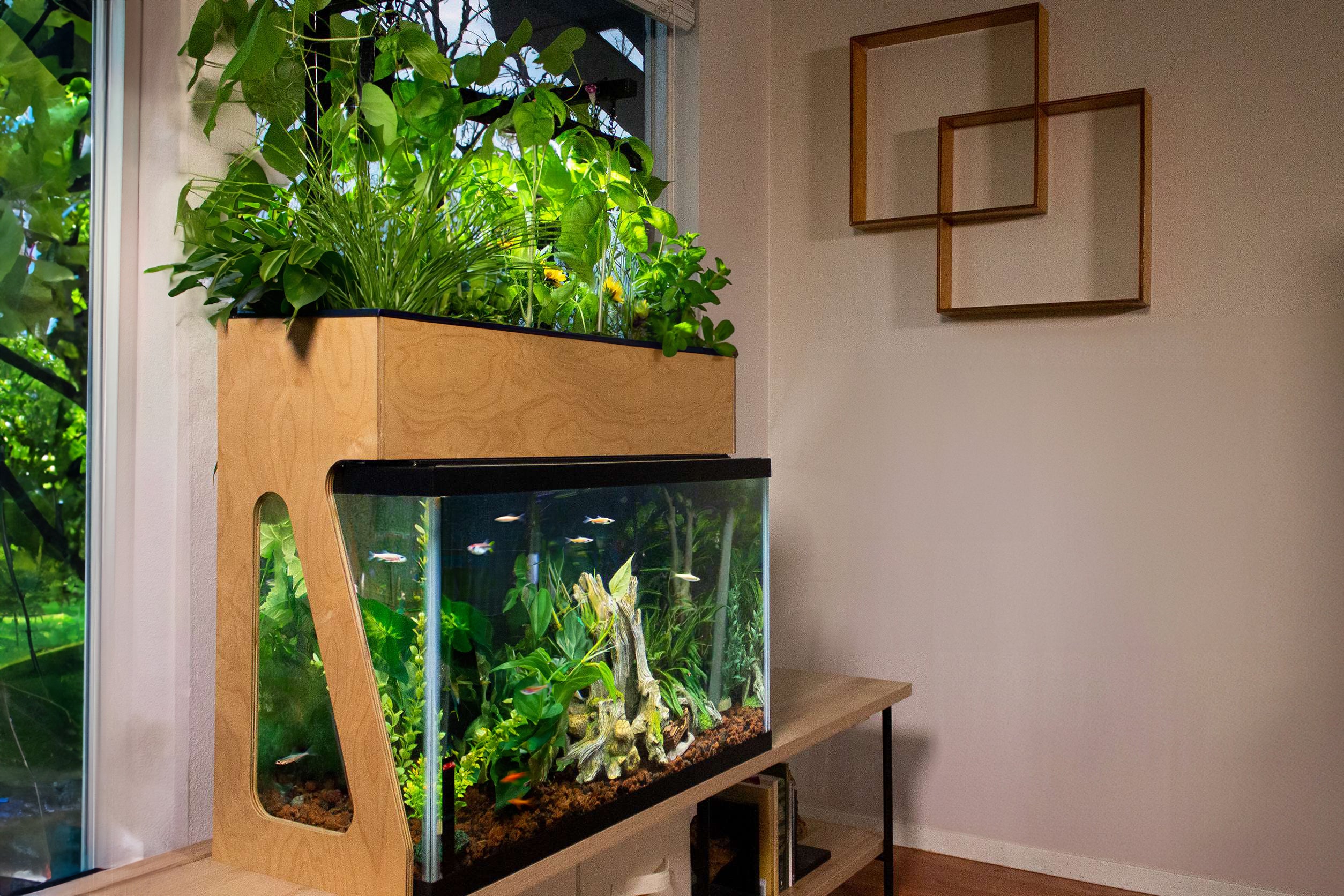

Central to the aquaponics system is the aquaponics fish tank, which serves as the habitat for fish and the primary source of nutrients for plants. Here, we examine the design considerations and functionality of aquaponics fish tanks, including size, shape, material, and water circulation systems. We discuss the importance of maintaining optimal water quality parameters, such as temperature, pH, and ammonia levels, to ensure the health and well-being of both fish and plants. Additionally, we explore different types of aquaponics fish commonly used in aquaponic systems, such as tilapia, trout, and catfish, and their suitability for various climates and growing conditions.
The Aquaponics Fish Tank: A Vital Component of Sustainable Farming
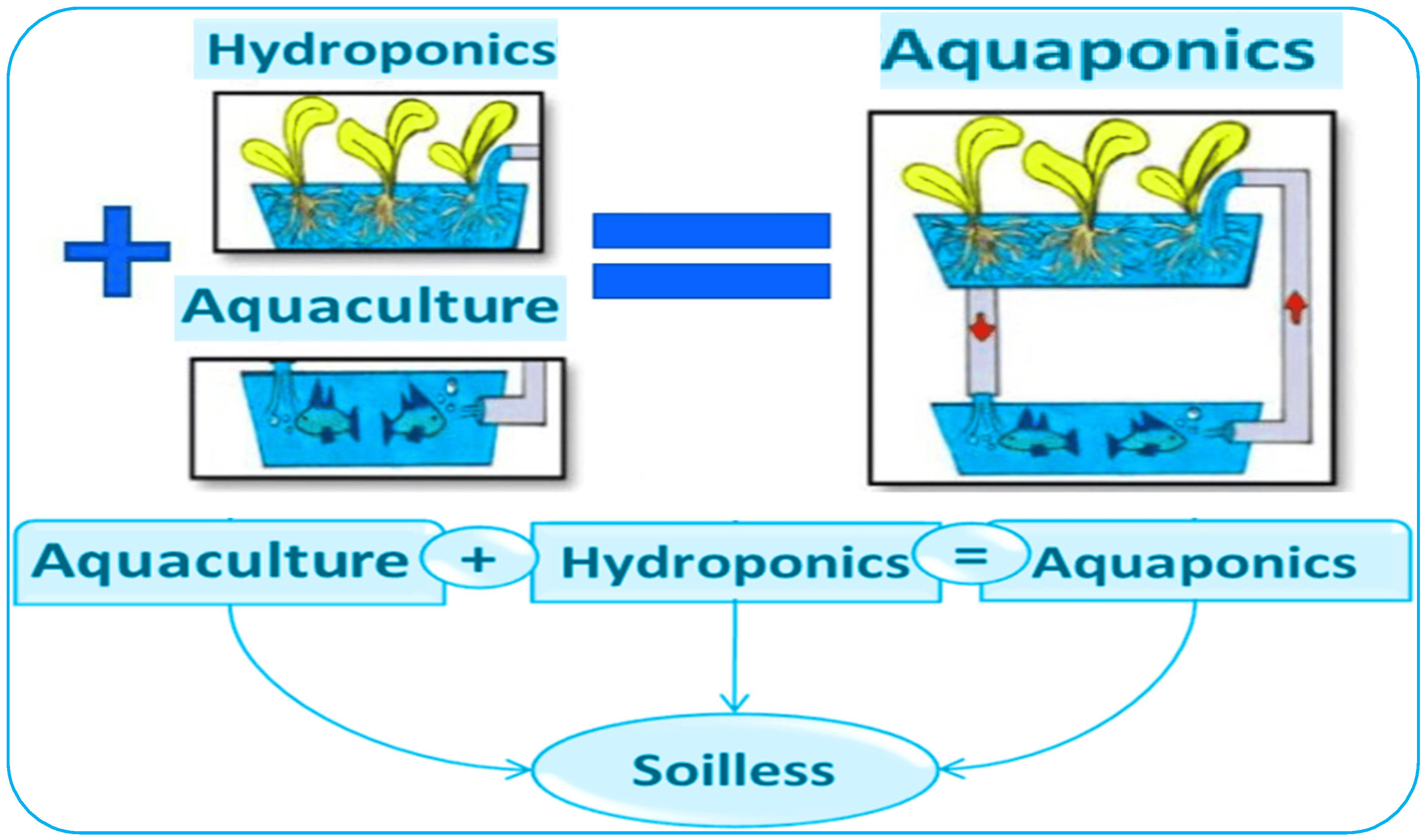
In the realm of sustainable agriculture, the aquaponics fish tank stands as a crucial element in creating thriving ecosystems that produce both fish and plants. This innovative system integrates aquaculture and hydroponics, fostering a symbiotic relationship where fish waste nourishes plants, and plants purify water for the fish. Let’s delve deeper into the significance of the aquaponics fish tank and its role in sustainable farming practices.
The Hub of Nutrient Cycling and Ecosystem Balance

The aquaponics fish tank serves as the central hub where the magic of nutrient cycling takes place. In this dynamic environment, fish excrete waste, primarily ammonia, which is then broken down by beneficial bacteria into nitrites and nitrates. These nitrogen compounds serve as vital nutrients for plants, fueling their growth and development. As plants absorb these nutrients, they act as natural filters, removing toxins and purifying the water, thus creating a healthy and balanced ecosystem for both fish and plants to thrive.
Design Considerations and Functionality
Aquaponics fish tanks come in various shapes, sizes, and materials, tailored to suit the needs of different setups and environments. Tanks may be constructed from materials such as glass, acrylic, or food-grade plastics, offering durability, transparency, and versatility. Water circulation systems, including pumps and filtration mechanisms, ensure proper oxygenation and nutrient distribution throughout the tank, promoting optimal conditions for fish and plant health. Temperature control features may also be incorporated to maintain stable water temperatures, further enhancing the well-being of aquatic inhabitants.
Diverse Fish Species and Their Contributions
Aquaponics fish tanks support a diverse array of fish species, each playing a unique role in the ecosystem. Commonly used fish species include tilapia, trout, catfish, and carp, chosen for their resilience, rapid growth, and compatibility with aquaponics systems. Fish not only provide valuable nutrients for plants but also serve as a sustainable protein source for human consumption. Additionally, certain species, such as tilapia, are known for their ability to thrive in diverse environmental conditions, making them well-suited for aquaponics setups.
Benefits for Farmers and Enthusiasts
The benefits of aquaponics fish tanks extend far beyond their functional role in food production. These tanks offer a sustainable and efficient method of growing fresh produce year-round, regardless of climate or geographical location. By eliminating the need for soil and synthetic fertilizers, aquaponics reduces environmental impact and conserves resources, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional agriculture. Moreover, aquaponics fish tanks can be integrated into existing food production systems, offering opportunities for diversification and resilience in the face of environmental challenges.
Versatility and Applications
Aquaponics fish tanks are not limited to food production; they also find applications in ornamental and educational settings. Tanks can be customized with decorative elements to create visually stunning displays that enhance indoor and outdoor spaces. Additionally, aquaponics serves as an educational tool for teaching students about ecosystems, sustainability, and the interconnectedness of living organisms, fostering a deeper appreciation for the natural world.
Benefits of Aquaponics Fish Tanks
Aquaponics fish tanks offer a multitude of benefits that make them an attractive option for sustainable farming. In this section, we outline the advantages of aquaponics fish tanks, including:
- Efficient Use of Resources: Aquaponics systems use less water and land compared to traditional farming methods, making them highly resource-efficient.
- Organic and Chemical-Free: Aquaponics relies on natural processes to fertilize plants, eliminating the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
- Year-Round Production: Aquaponics allows for year-round cultivation of plants in controlled environments, providing a steady supply of fresh produce regardless of seasonal changes.
- Diverse Crop Selection: Aquaponics systems can grow a wide variety of crops, including vegetables, herbs, fruits, and ornamental plants, offering farmers flexibility and versatility in crop selection.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: By minimizing the use of chemical inputs and reducing water consumption, aquaponics helps mitigate environmental pollution and conserve natural resources.
Applications of Aquaponics Fish Tanks
Aquaponics fish tanks have diverse applications across various sectors, including agriculture, aquaculture, education, and urban farming. Here, we explore the different ways in which aquaponics fish tanks are being utilized:
- Commercial Farming: Aquaponics systems are increasingly being adopted by commercial farmers to produce high-value crops for local markets, restaurants, and grocery stores.
- Home Gardening: Aquaponics fish tanks are popular among home gardeners and hobbyists looking to grow their own fresh produce in limited space.
- Educational Programs: Aquaponics serves as an educational tool for teaching students about sustainable agriculture, ecosystem dynamics, and environmental stewardship.
- Research and Development: Aquaponics research contributes to advancements in aquaculture, hydroponics, and sustainable farming practices, driving innovation and technological improvements in the field.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its many benefits, aquaponics also presents challenges and considerations that farmers and practitioners must address. In this section, we discuss common challenges such as:
- System Management: Maintaining optimal water quality and system balance requires careful monitoring and management of various parameters, including pH, temperature, and nutrient levels.
- Initial Investment: Setting up an aquaponics system, including the fish tank, filtration system, and grow beds, involves upfront costs that may deter some farmers from adopting this technology.
- Technical Expertise: Successful aquaponics farming requires knowledge and skills in fish husbandry, plant cultivation, water chemistry, and system management, posing a learning curve for beginners.
- Regulatory Compliance: Aquaponics farmers must comply with regulations governing water quality, fish health, food safety, and environmental protection, which vary by region and jurisdiction.
Future Directions and Innovations
As the field of aquaponics continues to evolve, new technologies and innovations are shaping the future of sustainable farming. In this section, we explore emerging trends and developments in aquaponics fish tank design, such as:
- Automation and Monitoring: Advances in sensor technology and automation systems enable real-time monitoring and control of aquaponics systems, improving efficiency and productivity.
- Integration of Renewable Energy: Integration of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power reduces reliance on conventional energy sources and enhances the sustainability of aquaponics operations.
- Vertical Farming: Vertical aquaponics systems maximize space utilization and crop production by stacking grow beds vertically, making them ideal for urban environments with limited land availability.
- Closed-Loop Systems: Closed-loop aquaponics systems minimize water consumption and nutrient loss by recirculating and reusing water within the system, reducing environmental impact and operating costs.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, aquaponics fish tanks represent a revolutionary approach to sustainable farming that harnesses the power of nature to produce healthy, nutritious food while minimizing environmental impact. By integrating
For More Information Please Visit These Websites Craiyon And Arturia





