Bringing Ideas to Life: Exploring the World of 3D Modeling
Table of Contents
Dive into the world of 3D modeling! Explore how it works, its uses across various industries, and popular software options to bring your ideas to life.
What is 3D modeling?

3D modeling is the process of creating a digital representation of a three-dimensional object. This is done using specialized software that allows you to manipulate points, lines, and shapes in a virtual space. The resulting model can be used for a variety of purposes, such as:
- Visualization: Creating realistic images or animations of objects
- Simulation: Testing how objects interact with the physical world
- 3D printing: Creating physical objects from digital models
3D modeling can be used in many different industries, including:
- Architecture and engineering: Creating models of buildings, products, and machines
- Entertainment: Creating characters, props, and environments for video games and movies
- Manufacturing: Designing and prototyping products
History of 3D modeling

The history of 3D modeling traces back to the early days of computer graphics, even before computers could render them in real-time. Here’s a brief overview:
Early development (1960s-1980s)
The concept of 3D modeling emerged in the 1960s with the development of specialized software and hardware.
Early models were primarily used for engineering and scientific applications, with limited visual complexity.
Pioneering work in this period laid the foundation for future advancements.
Advancements and wider use (1990s-2000s)
The 1990s saw significant progress in 3D modeling software and hardware capabilities.
Increased processing power allowed for more complex and realistic models.
3D modeling became more accessible and adopted in various fields beyond engineering, like gaming and entertainment.
Continued evolution (2000s-present)
The last few decades have witnessed continued advancements in:
Software: More user-friendly interfaces, powerful features, and specialized software for different applications.
Hardware: Increased processing power and graphics capabilities for real-time rendering and complex simulations.
3D printing: Emergence of 3D printing technology, directly utilizing 3D models for physical object creation.
Today, 3D modeling plays a crucial role in various industries, including:
Architecture and engineering: Designing buildings, products, and machines.
Entertainment: Creating characters, props, and environments for games and movies.
Manufacturing: Designing and prototyping products.
Science and medicine: Visualizing complex structures and processes.
The field continues to evolve, with new technologies and applications emerging constantly.
Representation of 3D models
3D models can be represented in different ways, but two main categories are:
Solid models
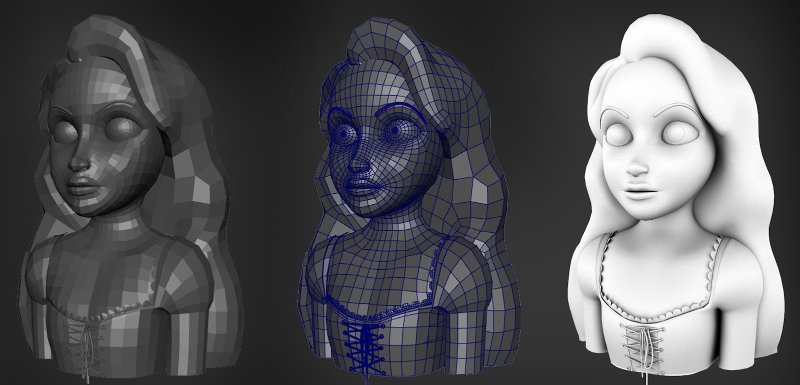
These define the entire volume of an object, like a rock. They’re often used in engineering and simulations where the object’s internal structure matters.
Shell models
These represent the surface of an object, like an eggshell. They’re commonly used in visuals like games and movies where only the outer appearance is important.
Both types can create objects that look the same, but they differ in how they’re created, edited, and used in different fields.
One common way to represent 3D models is with polygonal meshes. These are collections of connected shapes, like triangles, that form the surface of the model. Another way is with level sets, which are useful for objects that change shape a lot, like fluids.
The process of converting a mathematical representation of an object into a format suitable for rendering is called tessellation. This often involves breaking down the object into smaller shapes, like triangles in a mesh.
Process of 3D modeling

The 3D modeling process involves creating a digital representation of a 3D object. Here’s a breakdown of the general steps:
1. Choosing a technique
There are different techniques for creating 3D models, each with its own advantages and uses. Some common techniques include:
Polygonal modeling: Building the model from basic shapes like triangles.
Subdivision surface modeling: Creating smooth shapes from a base mesh.
NURBS modeling: Creating precise surfaces using mathematical formulas.
Boolean operations: Combining or subtracting simpler shapes to create complex forms.
Procedural modeling: Using algorithms to automatically generate the model based on defined rules.
Digital sculpting: Shaping a virtual object like working with clay.
2. Using software
3D modeling software provides tools to create, edit, and manipulate the model according to the chosen technique. Many software options are available, catering to different skill levels and purposes.
3. Refining the model
Once the basic shape is created, details like textures, materials, and lighting are added to enhance the model’s realism or visual appeal.
4. Exporting the model
The finished model can be exported in various formats for use in other applications like games, simulations, or 3D printing.
It’s important to note that this is a general overview, and the specific process can vary depending on the complexity of the model, the chosen technique, and the intended use.
Software for 3D modeling

3D modeling software allows you to create digital representations of three-dimensional objects. These programs are used in various industries, including:
Engineering: Designing and prototyping products
Architecture: Creating models of buildings and other structures
Entertainment: Creating characters, props, and environments for video games and movies
Simulation: Simulating the behavior of physical objects
There are many different 3D modeling software programs available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some popular options include:
- Blender (free and open-source)
- Maya (commercial)
- Solidworks (commercial)
The best software for you will depend on your specific needs and budget. If you’re just starting out, a free program like Blender might be a good option. If you have more advanced needs, a commercial program like Maya or Solidworks may be better suited.
Summary
3D modeling is creating digital 3D objects using specialized software. It’s used for various purposes like visualization, simulation, and 3D printing. Different techniques like polygonal modeling and sculpting are used to create these models. Popular software options include Blender, Maya, and Solidworks.
For More Information Please Visit These Websites Craiyon And Arturia