Ops: Keeping Things Running Smoothly in Business, Software Development, and IT
Table of Contents
Ops: The secret sauce behind smooth operations in business, software development, and IT. Learn what Ops means and its benefits across different fields.
What Does Ops Mean?

Ops stands for operations. It’s a general term used in various contexts to describe the activities that ensure something functions smoothly. Here are some examples:
In business
Ops refers to the day-to-day activities of running a company, like managing production, supply chains, and customer service.
In software development
Ops involve deploying, maintaining, and monitoring software systems.
In IT
Ops encompass managing computer networks and infrastructure.
Product Ops

Product Ops is a field focused on ensuring a product’s success. This involves activities like market research, quality checks, and improving efficiency. Product Ops teams collaborate across various departments to bring a product from concept to launch and beyond, ensuring it meets customer needs and integrates smoothly within the company.
5 Business Challenges that Product Ops Will Be Better?
Product operations (product ops) help businesses address various challenges in bringing products to market and ensuring their success. Here are five examples:
1. Process inefficiencies
Product ops can streamline workflows and communication across different teams involved in product development, such as engineering, design, and marketing. This can help reduce delays and improve overall efficiency.
2. Data overload
Businesses often collect a lot of data, but it can be difficult to analyze and use it effectively. Product ops can help by developing systems to organize and analyze data, and by presenting insights in a clear and actionable way.
3. Inconsistent product experiences
As products evolve, it’s important to maintain a consistent user experience across different platforms and features. Product ops can help by establishing guidelines and best practices for product development, ensuring a cohesive experience for users.
4. Difficulty measuring product success
Defining and measuring the success of a product can be complex. Product ops can help by establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) and tracking relevant metrics to evaluate product performance and identify areas for improvement.
5. Challenges in scaling products
As products gain traction, businesses may face challenges in scaling their operations to meet increasing demand. Product ops can help by identifying and implementing solutions to ensure the product can accommodate a growing user base.
By addressing these challenges, product ops can help businesses bring products to market faster, improve product quality and user experience, and achieve their overall business goals.
Benefits of Ops Across Different Fields
Ops, short for “operations,” refers to the practices and processes that ensure the smooth and efficient functioning of various systems and organizations. Here’s a look at its benefits in different areas:
In Business:
Increased Efficiency: Ops helps streamline workflows, automate tasks, and optimize resource allocation, leading to faster completion times and reduced costs.
Improved Decision-Making: By providing data-driven insights and performance metrics, Ops empowers businesses to make informed decisions based on fact, not guesswork.
Enhanced Customer Experience: Ops ensures smooth delivery of services and products, leading to better customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Reduced Risk: Proactive maintenance and risk management practices within Ops help prevent disruptions and minimize potential losses.
In Software Development:
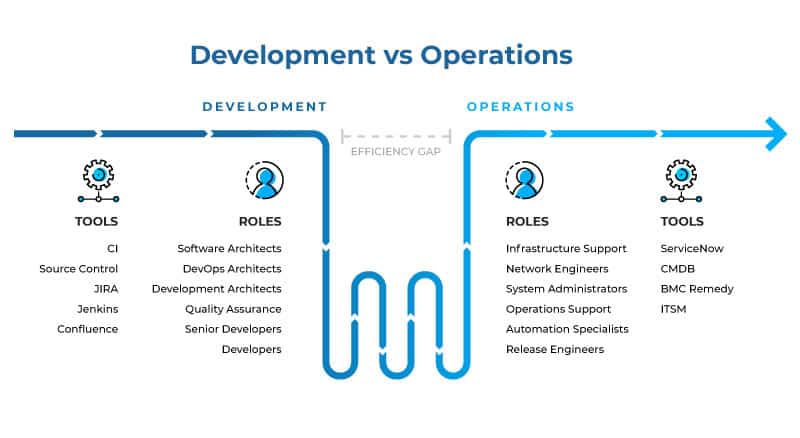
Faster Deployment and Delivery: Ops enables continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) practices, allowing for quicker and more frequent software releases.
Improved Software Quality: Ops promotes robust testing and monitoring procedures, leading to higher-quality software with fewer bugs.
Increased Scalability and Reliability: Ops helps design and manage systems that can handle growing user bases and changing demands, ensuring smooth operation.
Enhanced Collaboration: Ops fosters better communication and collaboration between developers, operations teams, and other stakeholders.
In IT:
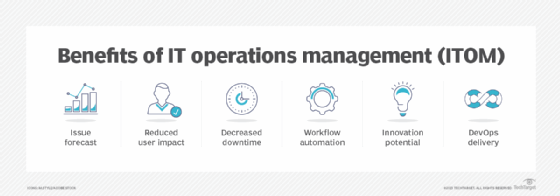
Improved Network Performance and Uptime: Ops practices like proactive monitoring and preventive maintenance help ensure network stability and minimize downtime.
Enhanced Security: Ops plays a crucial role in implementing and maintaining security measures, and protecting IT infrastructure and data from cyber threats.
Optimized Resource Utilization: Ops helps manage IT resources efficiently, ensuring they are allocated effectively to meet business needs.
Reduced Costs: Streamlined operations and proactive maintenance practices within Ops can help minimize IT-related costs.
Overall, Ops plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth functioning and efficiency of various systems and organizations. Its benefits range from increased productivity and cost savings to improved quality, reliability, and user experience.
Final Thoughts
Ops, short for “operations,” is a broad term encompassing the activities that keep things running smoothly. It’s found in various fields like business, software development, and IT, with specific applications in each area.
Product Ops focuses on ensuring a product’s success throughout its lifecycle, from market research to post-launch maintenance. By addressing challenges like inefficiencies and data overload, Product Ops helps businesses bring higher-quality products to market faster.
For More Information Please Visit These Websites Craiyon And Arturia